Crossed roller bearing applications are widely seen in precision equipment due to their compact size, exceptional rotational accuracy, and high rigidity. They offer strong deformation resistance and outstanding load-bearing capacity and can be flexibly designed to meet different working conditions. These features make them essential in high-end manufacturing sectors, including industrial robot joints and rotary parts, CNC rotary tables, machine tools, indexing tables, precision inspection platforms, medical imaging devices, astronomical telescopes, and large radar systems.
I. Structural Advantages of Crossed Roller Bearings
- High Rigidity and Easy Installation These bearings exhibit excellent structural rigidity and dimensional precision. They can be easily mounted onto mechanical assemblies using installation holes. Inside, spacer elements between the rollers prevent contact, enhancing smooth operation. This is particularly important for many crossed roller bearing applications requiring high reliability.
- Stable One-Piece Structure The bearing features a non-separable inner and outer ring design, which ensures high precision and rigidity while simplifying installation. Its compact form causes minimal interference with surrounding structures, making it suitable for medium—to high-speed operations. Internal spacers ensure smooth rotation and extended service life, contributing to the overall effectiveness of crossed roller bearing applications.
- Compact Design, Space-Saving Crossed roller bearings have a smaller outer diameter and narrower width than traditional bearings, making them ideal for applications requiring high-performance support in confined spaces. Moreover, their high manufacturing precision—reaching P4 or even P2 grade—enables more compact system designs and efficient use of space. These traits are crucial in crossed roller bearing applications where both space and precision are priorities.
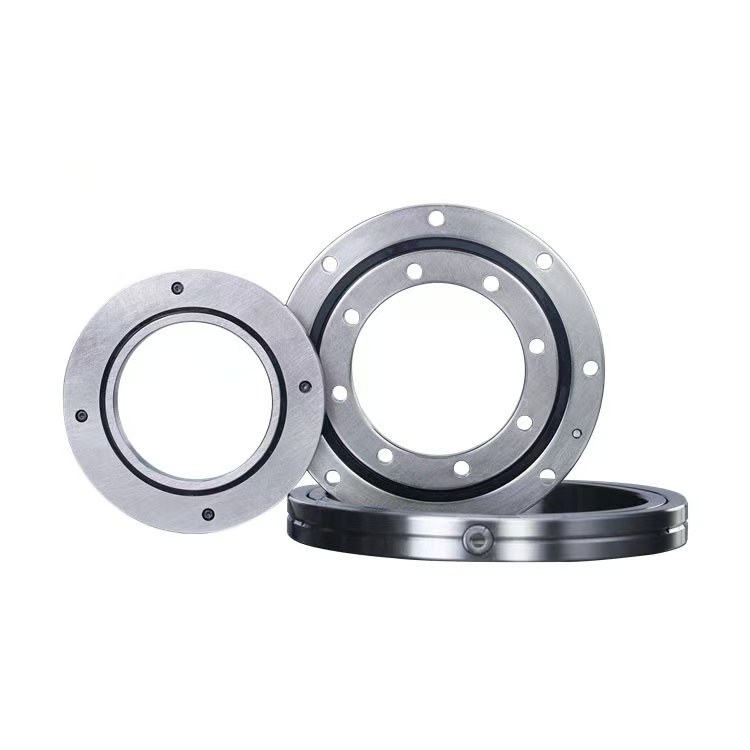

II. Working Principle and Structural Layout
The core structure of these bearings involves rollers arranged at 90° angles between the inner and outer rings. Spacers or separator blocks maintain precise intervals between the rollers. This crisscross layout allows the bearing to support substantial radial and axial loads simultaneously, preventing roller displacement, mutual friction, or seizure and ensuring low-torque operation. Additionally, the bearing clearance can be adjusted. Even when preload is applied, stable and high-precision rotation is maintained in demanding crossed roller bearing applications.
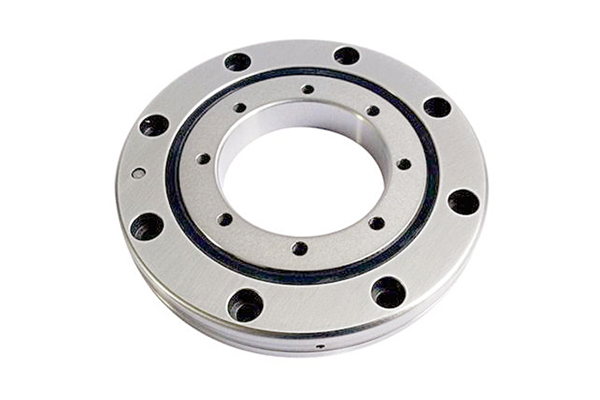

III. Performance Comparison with Traditional Bearings
Compared to conventional slewing or turntable bearings, crossed roller bearings offer several distinct advantages:
- 3 to 4 times higher rigidity and greater structural stability
- Line contact between rollers and raceways allows greater load capacity
- Flexible mounting from any direction to the main shaft
- Efficient operation reduces heat generation and lubricant consumption
- Negative clearance is achievable, greatly enhancing rotational accuracy
- Multi-directional load support simplifies structure and reduces equipment weight These benefits make crossed roller bearing applications superior in terms of performance and versatility.
IV. Broad Applications and Market Potential
These bearings are widely used in the following industries and equipment:
- Industrial robot joints and rotary actuators
- Visual inspection platforms and automated handling systems
- CNC machine tool turrets, indexing tables, and loading systems
With the continued advancement of automation and smart manufacturing, crossed roller bearing applications will play a key role in driving precision equipment toward higher accuracy and efficiency.
For more technical information or customized solutions regarding crossed roller bearing, contact us at [email protected]. Our team is ready to provide you with expert support and service.

 WhatsApp :
WhatsApp :  Phone : +1(617)816-5811
Phone : +1(617)816-5811  Skype :
Skype : E-mail :
E-mail :